In testing Test is considered successful if it completed without throwing an exception or test successfully validated expected results. Sometimes @test threw an exception that was expected and we mark test as success. TestNG can not just decide what should be the results of the Test by himself, So we need to provide the expected data and expected conditions.
TestNG use the concept of Assert from Java and can be used for adding validation and conditions in your test cases. Each assertion contains a boolean expression that you believe will be true when the assertion executes. If it is not true, the system will throw an error.
Assert statements are made of conditions and expressions where it validates the expressions given in the method. Mostly Asserts have two forms
1. An expression that has two value to compare.
Assert Expression1 : Expression2;
2. An expression as a boolean expression.
Assert Expression1;
How to use Assert in TestNG:
Below is the class which has 3 test methods Showing Success, Failure, and Failure by Exception.
package com.tutorial.testng;
import org.testng.Assert;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class AssertsInTestng {
@Test()
public void assertSuccessTest() {
// Comparing two same Strings.
Assert.assertEquals("testng", "testng");
}
@Test()
public void assertFailureTest() {
// Comparing two different Strings
Assert.assertEquals("testng", "java");
}
@Test()
public void exceptionFailureTest() {
String ptr = null;
// This line of code throws NullPointerException
ptr.equals("testng");
}
}
Results if you run this Java Class and check Success and Failures.
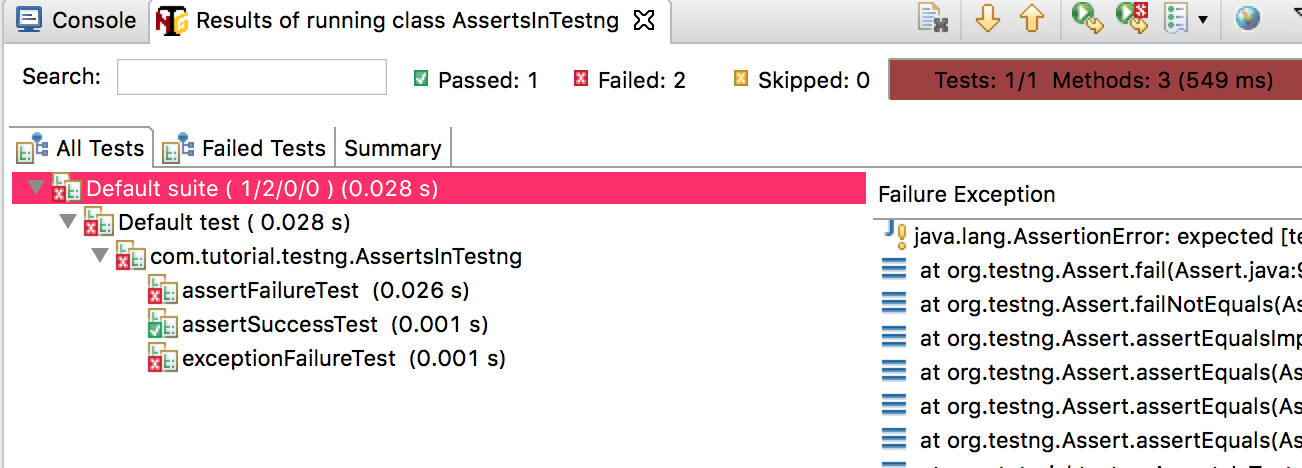
There are multiple methods in the org.testng.Assert Class. I have used a very basic method of comparing two Strings here. You can check the Assert Class in Java Docs for more methods you can use for expressions in your test. Some example:
- assertNotEquals
- assertNull
- assertNotNull
- assertSame
- assertTrue
Assert failures:
Whenever there is an assert failure in your @test, Assert Class throws an Exception of Exception class java.lang.AssertionError with a proper error message which is describing the test failure. Like :
java.lang.AssertionError: expected [testn] but found [testng]
Error messages are always helpful in understanding the Error in Test. You can also customize and provide your own error messages while creating Assert in your Test Class. Assertion error message has always been used when the assert condition fail.
@Test()
public void assertFailureTest() {
// Comparing two Strings with assertion error message
Assert.assertEquals("testng", "java","String objects are not equal,So Assert Failure");
}
Now the test failure message:
java.lang.AssertionError: String objects are not equal, So Assert Failure.
expected [java] but found [testng]